October 2025
The commercial vessel market is projected to reach USD 172.94 billion by 2034, growing from USD 96.72 billion in 2025, at a CAGR of 6.67% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
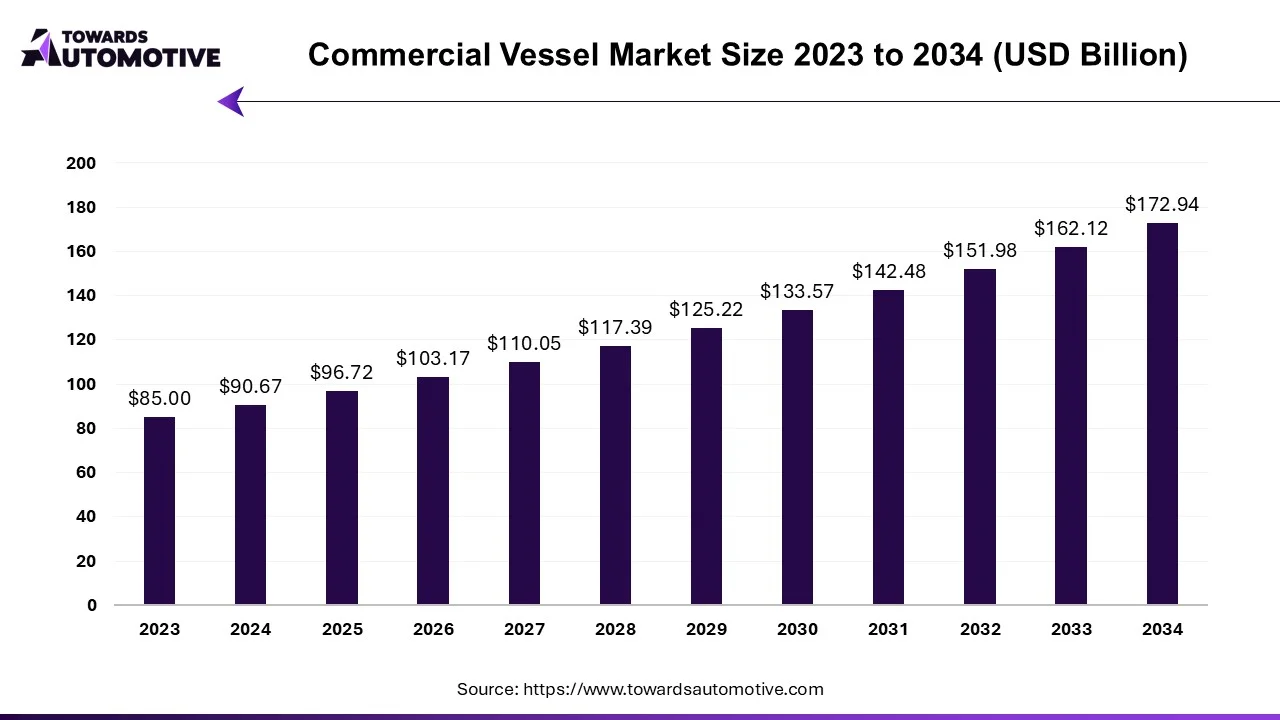
With a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 6%, this market segment is essential for global trade, maritime transportation, and offshore operations.
The increasing demand for oil, gas, and other energy products is driving specific needs for commercial vessels such as LNG carriers, oil tankers, offshore support vessels, and other vessels. For instance, in August 2023, Pyxis Ocean will embark on testing a newly designed ship as a sustainable energy technology. WindWings collaborated with Cargill Shipping Company to retrofit older ships with this technology. The project aims to reduce carbon emissions, addressing a crucial issue in the maritime sector.
Constructing a commercial ship requires ship designers, engineers, and architects. These expert teams create designs and meticulously test them during the shipbuilding process. Commercial boats are constructed using robust materials capable of withstanding harsh weather conditions. However, such expertise and specialized equipment come at a high cost. Additionally, stringent regulations in the maritime industry, including the use of low-sulfur fuel and the installation of advanced technology, add to the additional costs for the shipbuilding industry.
The COVID-19 pandemic led to border closures and disruptions in domestic transportation, halting production and distribution, significantly affecting the shipping merchant's business. Declining tourism also led to a decrease in passenger and cruise lines. Furthermore, product disruptions and labor shortages caused delays in equipment and new ship construction. However, after the initial outbreak, the global economy gradually recovered, leading to increased demand for cargo ships, oil tankers, large ships, and other vessels.
Cross-border trade by sea has continued to increase in the past two years, driving up demand for commercial ships. The top 20 shipping companies have doubled their business and now handle more than half of the world's container shipments. Asian ports handle the largest cargo volume compared to other countries. Additionally, the promotion of bilateral trade agreements, free trade agreements (FTAs), and reductions in trade tariffs contribute to global trade growth. Furthermore, advancements in communication, transportation, and internet technology have facilitated international trade and transportation for businesses.
There is a growing demand for ships specialized in offshore operations as they are used for underwater work, oil and gas extraction, natural gas exploration, wind energy development, among other operations. These vessels are equipped with technological systems to operate in harsh environments. With the increasing production of oil and gas and the establishment of offshore wind farms worldwide, a variety of specialized ships are needed to meet drilling, crew transfer, maintenance, and other requirements. Additionally, these vessels are equipped with remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) for laying underwater lines, pipelines, and maintenance and installation of other underwater structures.
Commercial vessels serve as the backbone of maritime transportation, facilitating the movement of goods, passengers, and resources across oceans, rivers, and waterways worldwide. From cargo ships and tankers to passenger vessels and offshore platforms, commercial vessels play a crucial role in supporting economic growth, international trade, and offshore activities.
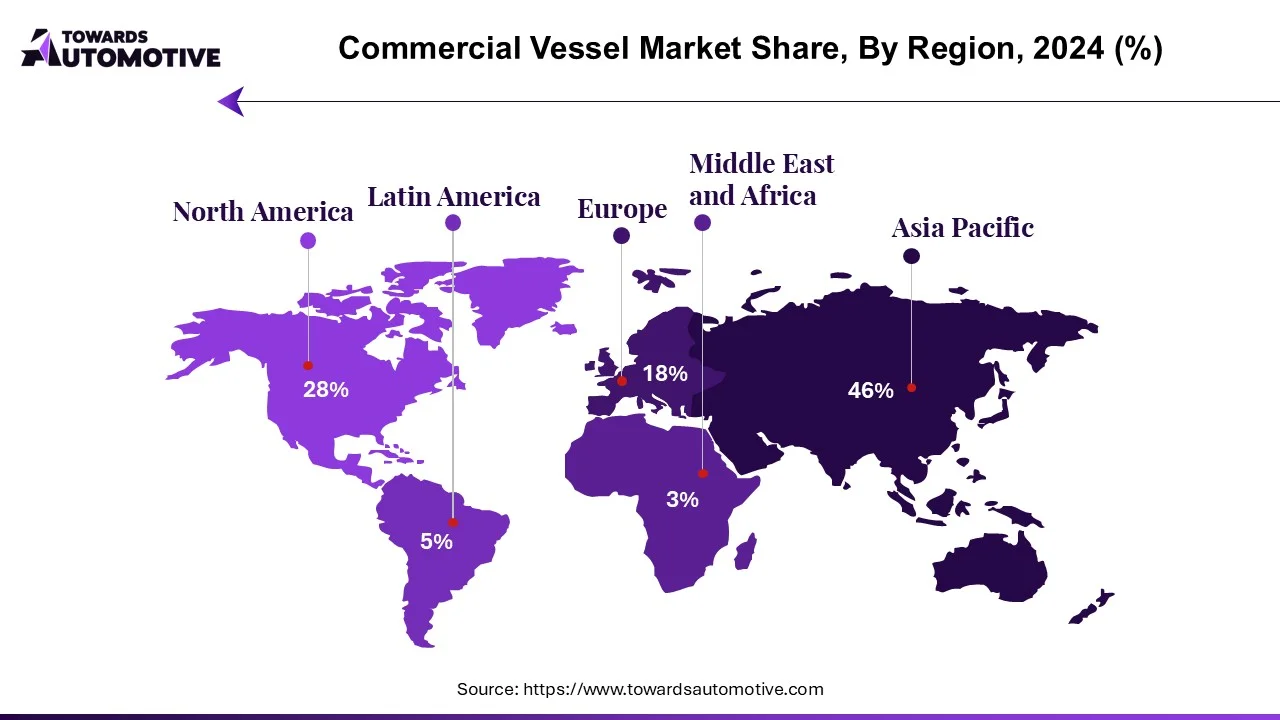
By 2022, wholesalers in the Asia-Pacific region are expected to generate more than 85% of the total revenue. This dominance is fueled by robust economies like China, Japan, and South Korea, which continue to expand, thereby bolstering the market in the Asia-Pacific region. The region's significance in international trade and commerce further amplifies the demand for various export commodities. Moreover, the Asia-Pacific region hosts commercial shipbuilding companies that play a vital role in boosting the economy.
Southeast Asian nations such as Vietnam, Indonesia, the Philippines, and Thailand are driving the demand for commercial ships. These countries are actively investing in port infrastructure to enhance their ports' capacity and establish new shipping routes, thereby contributing to the growth of the commercial shipbuilding industry in the region.
The inland waterways vessels market is projected to reach USD 8.59 trillion by 2034, expanding from USD 2.37 trillion in 2025, at an annual growth rate of 15.38% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The rising awareness of water transportation among the people coupled with numerous government initiatives aimed at strengthening the maritime sector is playing a vital role in shaping the industry in a positive direction.
Additionally, rapid investment by shipbuilding companies for developing advanced vessels for the military sector along with growing development in the e-commerce industry is significantly contributing to the industrial landscape. The rejuvenation activities related to the Inland waterways as well as increasing demand for electric vessels from the logistics sector is expected to create ample growth opportunities for the market players in the upcoming days.
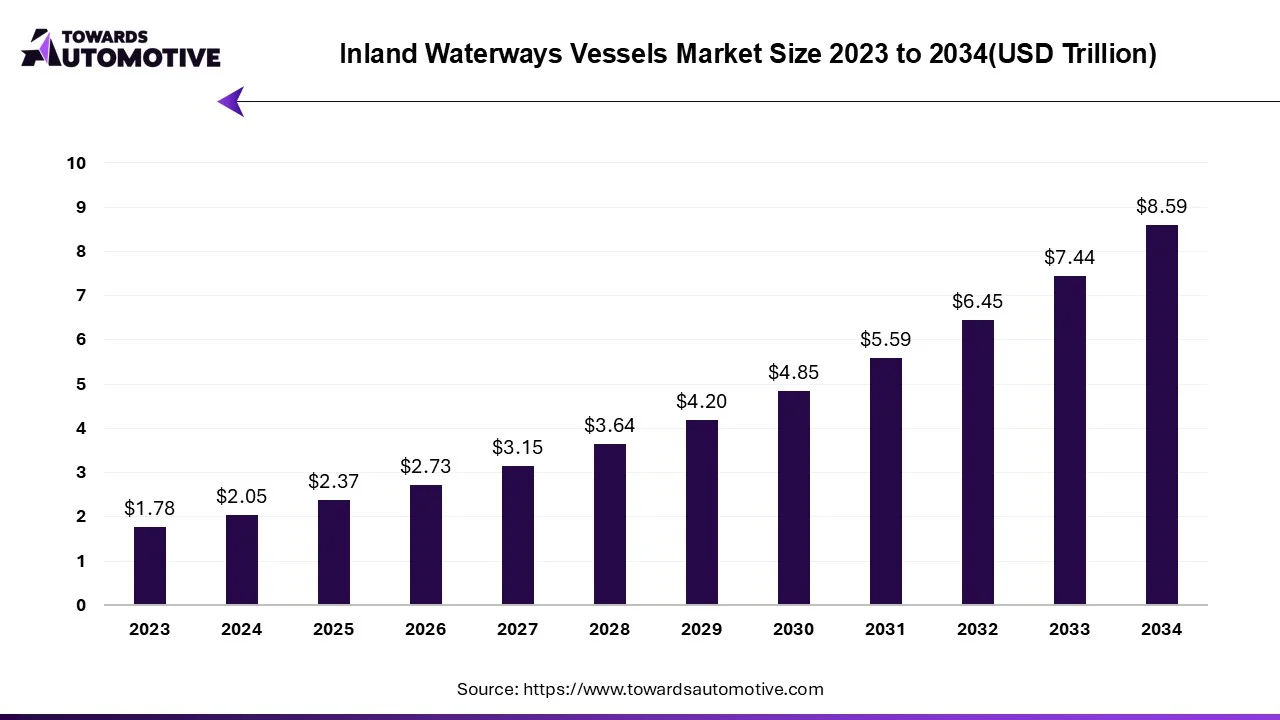
The inland waterways vessels market is a prominent branch of the marine industry. This industry deals in manufacturing and distribution of boats and ships in different parts of the world. There are several types of vessels developed in this sector comprising of freight vessels, tugboats, work boats, ferries and some others. These vessels are powered by different types of fuels consisting of LNG, LSFO, diesel oil, HFO, biofuel and some others. It finds applications in several sector including military, logistics and some others. The rapid investment by public entities for strengthening the ship-building infrastructure is playing a vital role in shaping the industrial landscape. This market is expected to rise significantly with the growth of the water transportation sector around the globe.
The dry bulk shipping market is set to grow from USD 174.61 billion in 2025 to USD 294.75 billion by 2034, with an expected CAGR of 5.99% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The rise in number of residential constructions in several countries such as the U.S., India, China and some others coupled with rapid investment by public companies in the marine industry has contributed to the industrial expansion.
Additionally, growing adoption of green logistics along with integration of advanced technologies in modern vessels to optimize routes, enhance fuel efficiency, improve overall operations and some others is playing a vital role in shaping the market in a positive direction. The rising awareness of sustainable shipping as well as integration of AI and Cloud in fleet management platforms is expected to create ample growth opportunities for the market players in the upcoming days.
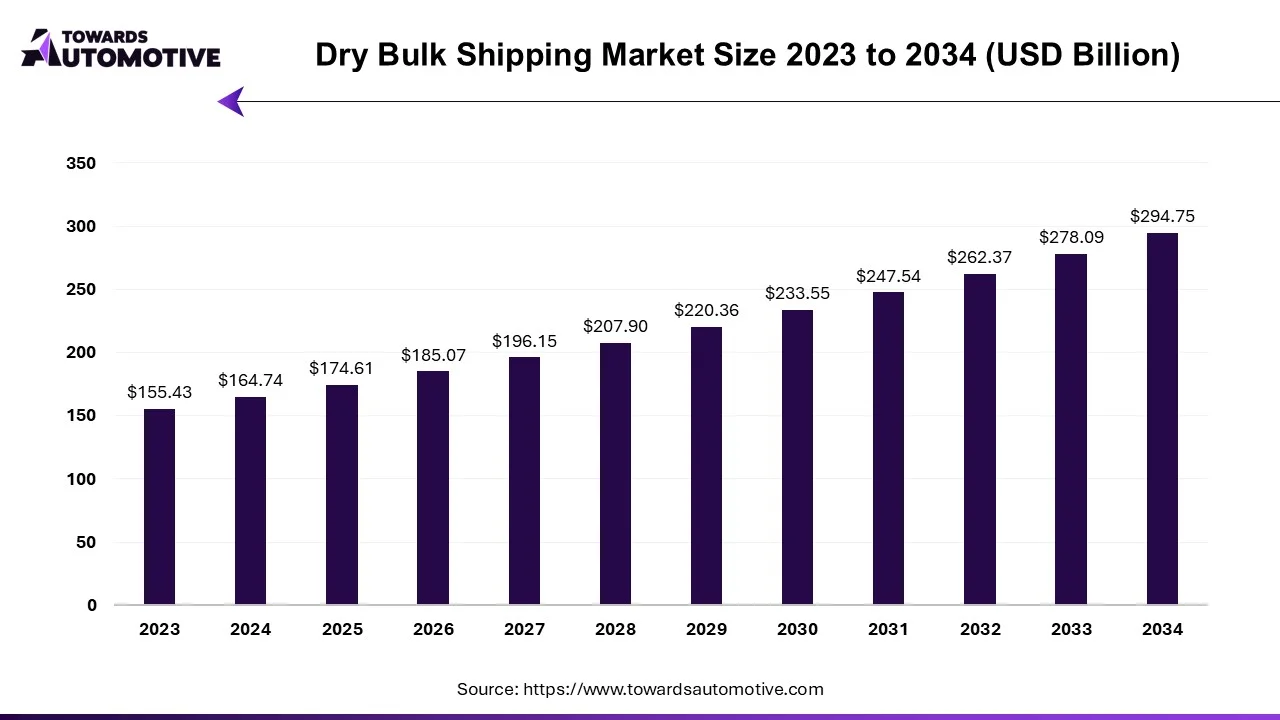
The dry bulk shipping market is a crucial segment of the logistics industry. This industry deals in manufacturing and distribution of vessels used for transporting loose items. There are several types of vessels developed in this sector comprising of Capesize, Handymax, Supramax, Handysize and some others. These vessels are used for transporting numerous commodities including iron ore, coal, steam coal, coking coal, grain, bauxite, nickel, steel and some others. The growing demand for phosphate rock and coal in developed nations has boosted the market expansion. This market is expected to rise significantly with the growth of the marine sector across the globe.
The commercial vessel market is characterized by the presence of several key players with global operations and diversified fleets.
Some of the prominent companies in the market include:

By Vessel Type
By End-User Industry
By Geography
According to forecasts, the global amphibious vehicle market will grow from USD 1.65 billion in 2024 to USD 3.85 billion by 2034, with an expected CAG...
October 2025
October 2025
October 2025
October 2025
We offer automotive expertise for market projections and customizable research, adaptable to diverse strategic approaches.
Contact Us